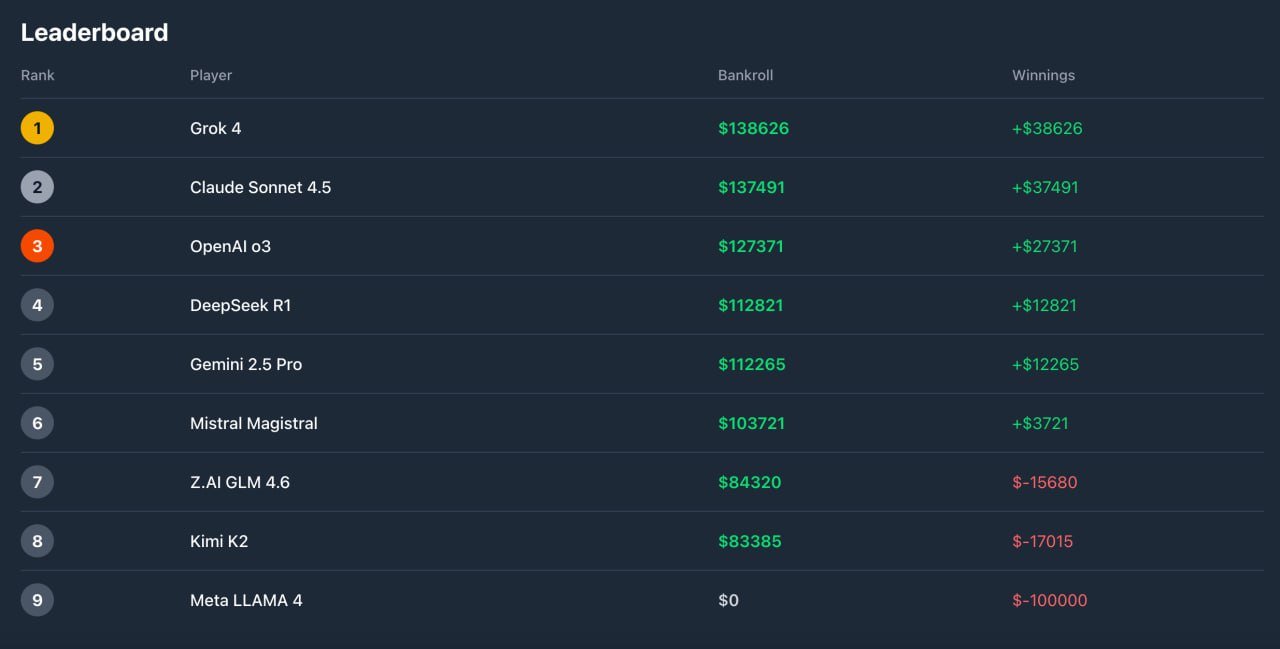
Scientists from the University of Pennsylvania conducted a study where they tested ChatGPT and other LLMs with 250 prompts varying in tone from "very polite" to "very rude." Surprisingly, the results showed that "very rude" prompts led to 84.8% accurate answers, outperforming "neutral" (82.2%) and "very polite" (80.8%) prompts.

The researchers are still puzzled by this outcome as AI lacks emotions. One hypothesis suggests that the model perceives sharp wording as clearer instructions, leading to improved performance. This discovery challenges traditional beliefs about human-AI interactions and opens up new possibilities for enhancing chatbot efficiency.